Reasons and solutions for lithium battery pack bulging
Aug,16,24
So far, lithium batteries have been widely used in the market due to their high energy ratio and high safety.
Although batteries like lithium batteries do not have the same high safety as polymer batteries,
they are relatively cheap due to their early development.
At the same time, many manufacturers can produce them, which leads to uneven safety.
The safety of lithium batteries is sometimes not guaranteed.
In addition, there are still certain safety hazards if used improperly or if the production level is limited, such as battery bulging.
So why does lithium battery experience bulging phenomenon?

Let's learn about the structure and composition of lithium battery packs, as well as some factors that affect them.
1、Basic structural analysis of lithium battery pack
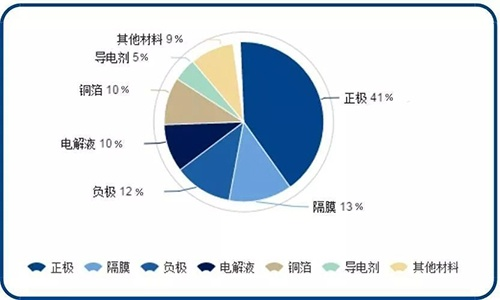
The main material composition of lithium battery pack includes positive electrode material,
negative electrode material, electrolyte, and separator (isolation material).
positive electrode
From the perspective of battery weight composition, positive electrode materials account for a large proportion (generally 70%~80%),
because the performance of positive electrode materials directly affects the performance of lithium-ion batteries,
and their cost directly determines the cost of the battery.
Positive electrode materials account for 30% to 40% of the cost of lithium-ion batteries
and directly affect the energy density and performance of lithium battery packs.
negative pole
The negative electrode material is composed of materials with lower potential relative to the positive electrode,
and has high specific capacity and good charge discharge reversibility,
thus maintaining good size and mechanical stability (without severe deformation) during lithium insertion.
Negative electrode materials mainly affect the efficiency and cycling performance of lithium battery packs,
and the performance of negative electrode materials directly affects the performance of lithium batteries.
Negative electrode materials account for about 10-20% of the total cost of lithium batteries. In terms of types of negative electrode materials,
they include carbon based negative electrodes and non carbon negative electrodes.
electrolyte
The electrolyte plays a role in transporting charges between the positive and negative electrodes (similar to carrier waves in radio),
and has a high ionic conductivity, generally reaching 1x10-3-2x10-2 S/cm.
It affects factors such as energy density, wide temperature application, cycle life, power density, and safety performance of lithium battery packs.
the diaphragm
The diaphragm has a certain pore size and porosity, ensuring low resistance and high ion conductivity,
good permeability to lithium ions, good infiltration of electrolyte and sufficient liquid absorption and moisturizing ability, maintaining ion conductivity,
and electronic insulation to ensure mechanical isolation between positive and negative electrodes.
In addition, it should have sufficient mechanical properties such as puncture strength, tensile strength,
resistance to electrolyte corrosion, and sufficient electrochemical stability.
Power batteries have higher requirements for separators and usually use composite membranes.
2、Why do lithium battery packs bulge?
There are three main reasons for lithium battery bulging:
The first type: Manufacturer's production and manufacturing process issues
Due to the large number of manufacturers, many of them create harsh production environments
and eliminate equipment and machinery in order to save costs.
As a result, the coating of the battery is uneven and dust particles are mixed into the electrolyte.
All of these may cause lithium battery packs to swell during user use, and even pose greater danger.
Second type: User's daily usage habits
The second type lies in the user themselves. Improper use of lithium battery products,
such as overcharging or discharging, or continuous use in extremely harsh environments,
can also cause lithium batteries to swell.
The third type: long-term disuse and improper storage
If any product is not used for a long time, its original performance will basically decline,
and the battery will not be used for a long time without proper storage.
When it is exposed to air for a long time without use and fully charged.
Due to the conductivity of air to a certain extent,
prolonged exposure to it is equivalent to direct contact between the positive and negative electrodes of the battery,
leading to a chronic short circuit.
Once short circuited, it will generate heat, decompose or even vaporize some electrolytes, resulting in bulging.
The reasons for bulging caused by overcharging and overdischarging are as follows:
Overcharging induced bulging: Overcharging can cause all lithium atoms in the positive electrode material to run into the negative electrode material,
causing the originally full grid of the positive electrode to deform and collapse, which is also a major reason for the decrease in lithium battery capacity.
During this process, the amount of lithium ions in the negative electrode increases,
and excessive accumulation causes lithium atoms to grow tree stumps and crystals, leading to swelling of the lithium battery.
Overdischarge induced bulging: During the first charge and discharge process of liquid lithium-ion batteries,
the electrode material reacts with the electrolyte at the solid-liquid interface, forming a passivation layer covering the surface of the electrode material.
The passivation layer film formed can effectively prevent the passage of electrolyte molecules,
but Li+can be freely embedded and removed through the passivation layer, which has the characteristics of solid electrolyte.
Therefore, this passivation film is called "solid electrolyte interface", or SEI for short.
SEI film has a protective effect on negative electrode materials,
making the material structure less prone to collapse and increasing the cycling life of electrode materials.
The SEI film is not static, and there may be slight changes during the charging and discharging process,
mainly due to reversible changes in some organic compounds.
After excessive discharge of the battery, the SEI film undergoes reversible damage,
which protects the negative electrode material and causes the negative electrode material to collapse, resulting in bulging phenomenon.
These two factors can cause a violent reaction similar to a short circuit to occur inside the battery during use,
generating a large amount of heat, which in turn leads to electrolyte decomposition and gasification, causing the battery to bulge.
3、How to safely handle lithium battery bulges?
1.)Starting to replenish power after using up about half of the battery,
and in rare cases only performing a complete discharge and full charge maintenance
(such as fully discharging and charging once after several months to six months of use, frequent full charging and discharging can easily lead to crystal growth),
can greatly reduce the amount of crystals and significantly slow down the bulging phenomenon.
2.)The bulging lithium battery can be directly discarded because its power capacity is already very small and it has little power after a short circuit.
3) Lithium battery packs generally need to be professionally recycled to avoid pollution.
If they cannot be disposed of, they should be thrown into the classified recycling bin.
The above are the reasons for lithium battery bulging and how to handle the lithium battery pack correctly after bulging.






