Lithium carbonate prices hit a new low, why bother with bottom support?
Aug,05,24
The price of lithium carbonate has repeatedly hit new lows, and market attention has increased.
The current price has reached the 90th percentile of the full cost of lithium resources, however, there has been no significant slowdown on the supply side.
Therefore, this article will further explore the future supply situation and the cost support position of prices.
In terms of integrated production capacity, although some manufacturers have announced shutdowns for maintenance, the impact on production is not significant.
Supply continues to increase, and the capacity on the right side of the cost curve is being tested.
From the perspective of external production capacity, the production power is mainly driven by profits, and with the narrowing of profit margins, it may slow down in the future.
Looking at the second half of the year, although there are still expectations of "golden September and silver October" and "year-end surge" demand in the market,
the temporary rebound in demand is indeed expected to drive the price center upward.
The expectation of restocking in August is still high, and the demand during the peak season is expected to drive a price rebound.
However, due to inventory pressure, we need to be relatively cautious about the strength of the rebound.
However, in reality, the global supply and demand pattern of lithium carbonate is difficult to reverse.
From the perspective of mining projects, the price support brought by higher cost projects is at 80000 yuan/ton,
which is the 90th percentile of the full cost of the mine.
The global lithium resource supply-demand balance is estimated to have a marginal cost price of 77000 yuan/ton,
which is approximately at the 86th percentile;
The global supply and demand balance of lithium carbonate is estimated to have a marginal cost price of 65000 yuan/ton,
which is approximately at the 75th percentile. Therefore, we believe that 80000 yuan/ton is the first cost support.
If the short-term price drops below 80000 yuan/ton and rebounds, it will not cause a significant reduction in production.
However, if the long-term average price is at or below 77000 yuan/ton in the market, it is more likely to trigger a contraction in supply.
If the price further drops, market prices with a long-term average price of 65000 yuan/ton or less may be able to reverse the supply
and demand structure through a significant reduction in mining production.
Recently, the price of lithium carbonate has repeatedly hit new lows, causing widespread market attention.
As of August 1st, the futures price closed at 80850 yuan/ton with a minimum of 80450 yuan/ton.
According to the analysis of the complete cost of global lithium resources, the current price has reached the 90th percentile of the complete cost of lithium resources.
However, despite a decrease in production in the past two weeks, the supply side is expected to maintain positive growth in August production.
Therefore, this article will further explore the future supply situation and the cost support position of prices.
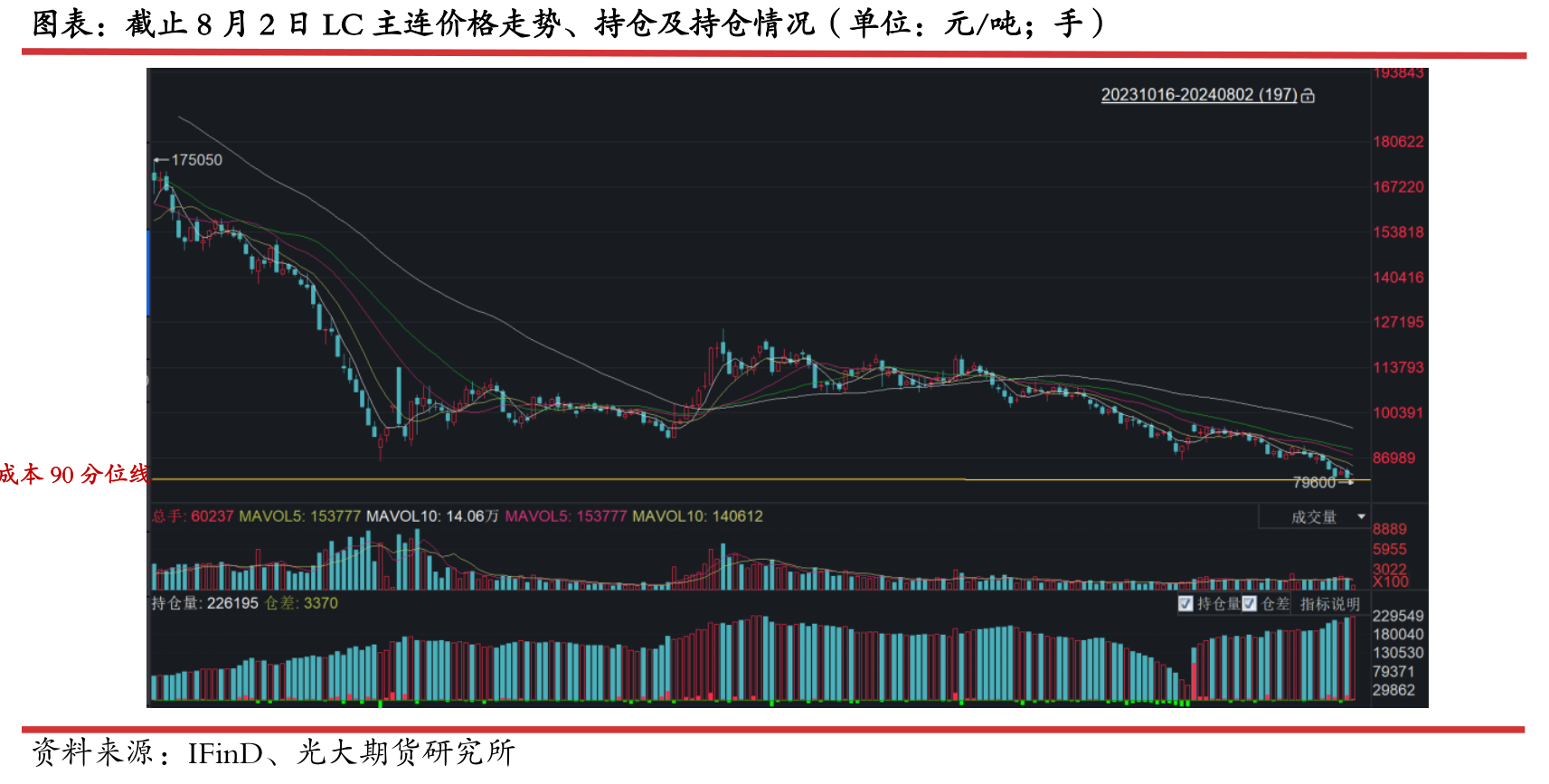
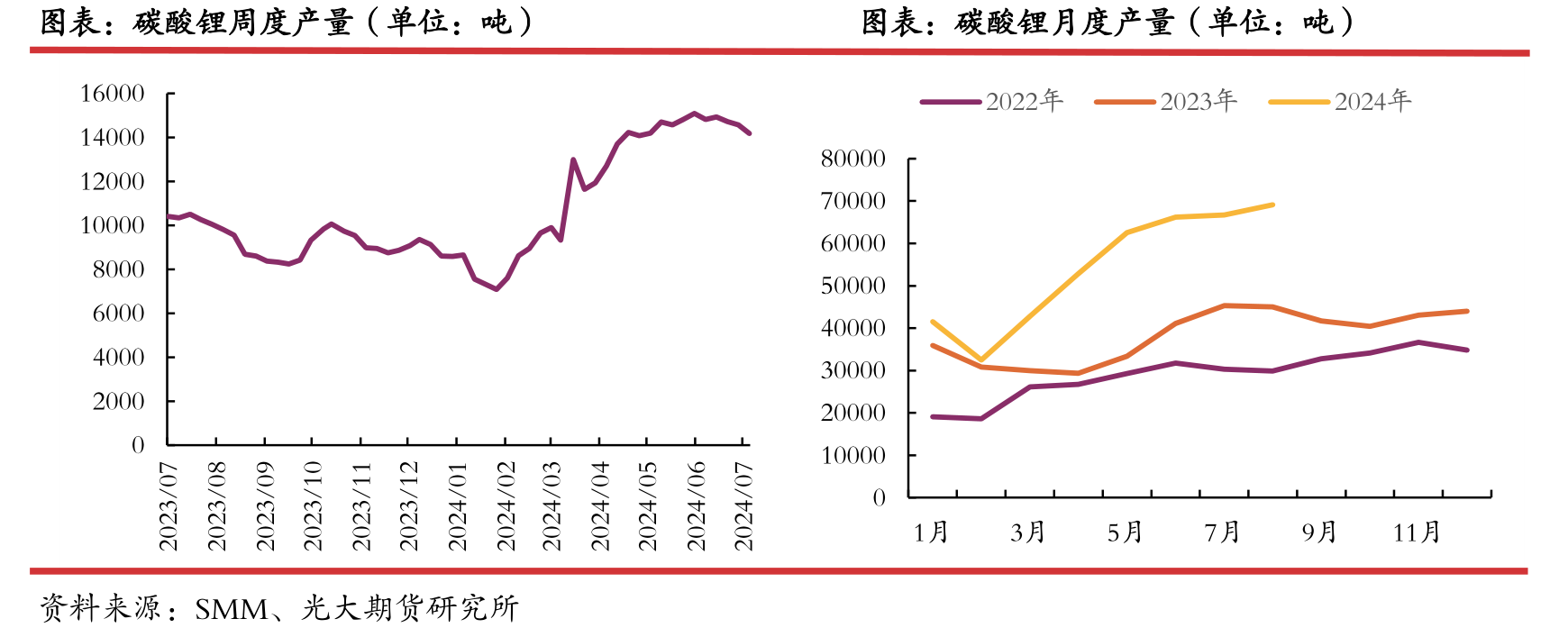
1、 Integrated supply is being tested, and external procurement may decrease
In terms of integrated production capacity, the supply continues to increase, and the capacity on the right side of the cost curve is being tested.
According to company announcements and third-party data research, some domestic manufacturers have had certain production reduction/maintenance plans since July,
but as of the time of publication, the overall reduction has not had a significant impact on the current supply-demand balance.
At the same time, there are still lithium mining projects in Africa and salt lake projects in South America climbing or being put into operation this year.
Therefore, whether there will be a significant reduction in production on the supply side depends on the production capacity on the right side of the cost curve on the resource side.
From the perspective of external production capacity, the production power is mainly driven by profits, and with the narrowing of profit margins, it may slow down in the future.
Since the end of last year, the structure of the lithium carbonate futures market has shifted from B to C.
In such a market and model, it can be considered that by buying "cash" in the near month contract and selling "futures" in the main contract, outsourcing companies can obtain certain price difference returns.
At the same time, the pricing model of lithium ore trade has changed, and the purchasing price at the mining end has shifted from Q - to M+structure.
As of now, some have also calculated based on the price of lithium salt. In a declining market, lower purchasing costs can increase profits.
However, there is still a certain lag between the prices of raw materials and finished products, which leads to a large profit margin when prices rise.
After the price turning point, the profit margin begins to shrink, and even invert. Moreover, the lower the price range, the less likely the lithium ore quotation/auction price/transaction price is to fall.
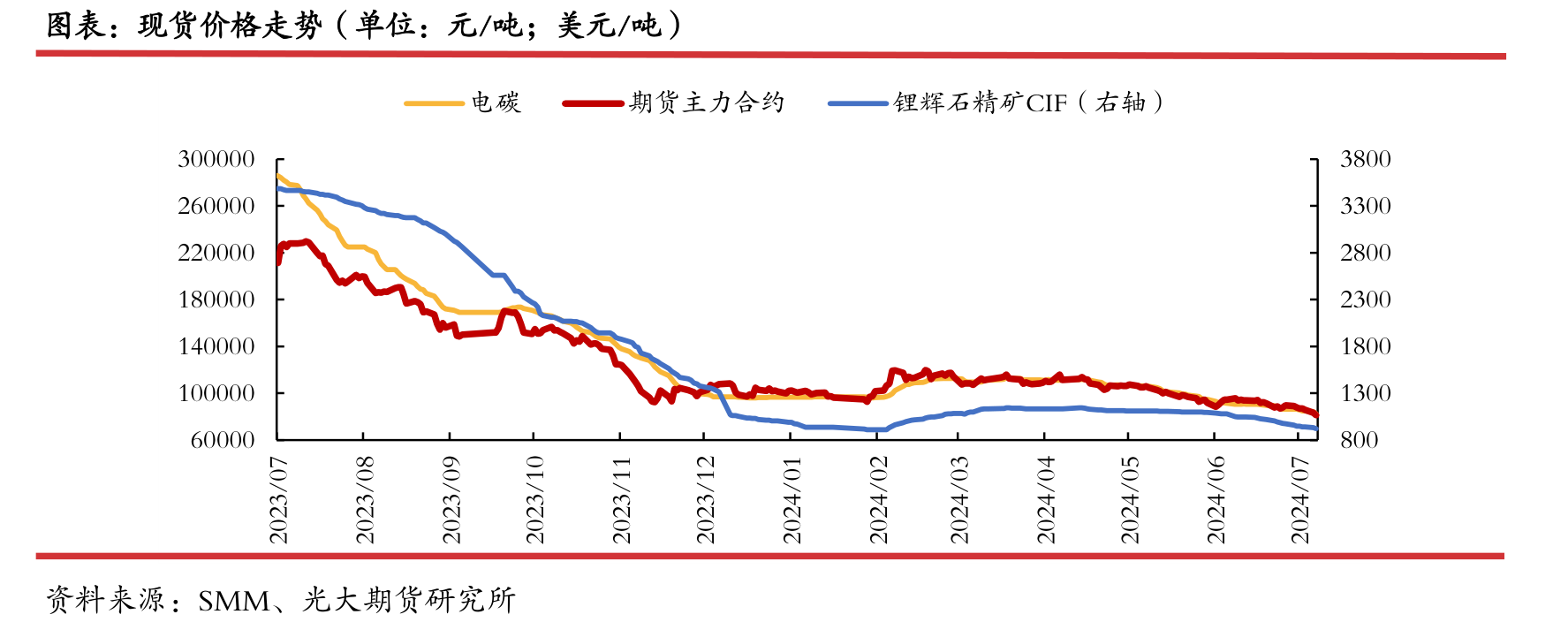
For example, during this year's "Gold Three Silver Four" market,
lithium mining processing profits have increased, and if one chooses to participate in the futures market for synchronous selling, it can achieve a better level of profit locking.
After the peak season, the prices of lithium carbonate and lithium ore quickly fell,
and the price of lithium carbonate fell even more and at a faster rate, resulting in a narrower profit margin for external mining and processing of lithium carbonate,
whether based on long-term agreements (three party quotes * discounts) or by participating in futures market locking.
According to SMM's statistics on external mining profits, external lithium concentrate has been losing money since mid June and has remained in a loss making state to this day.
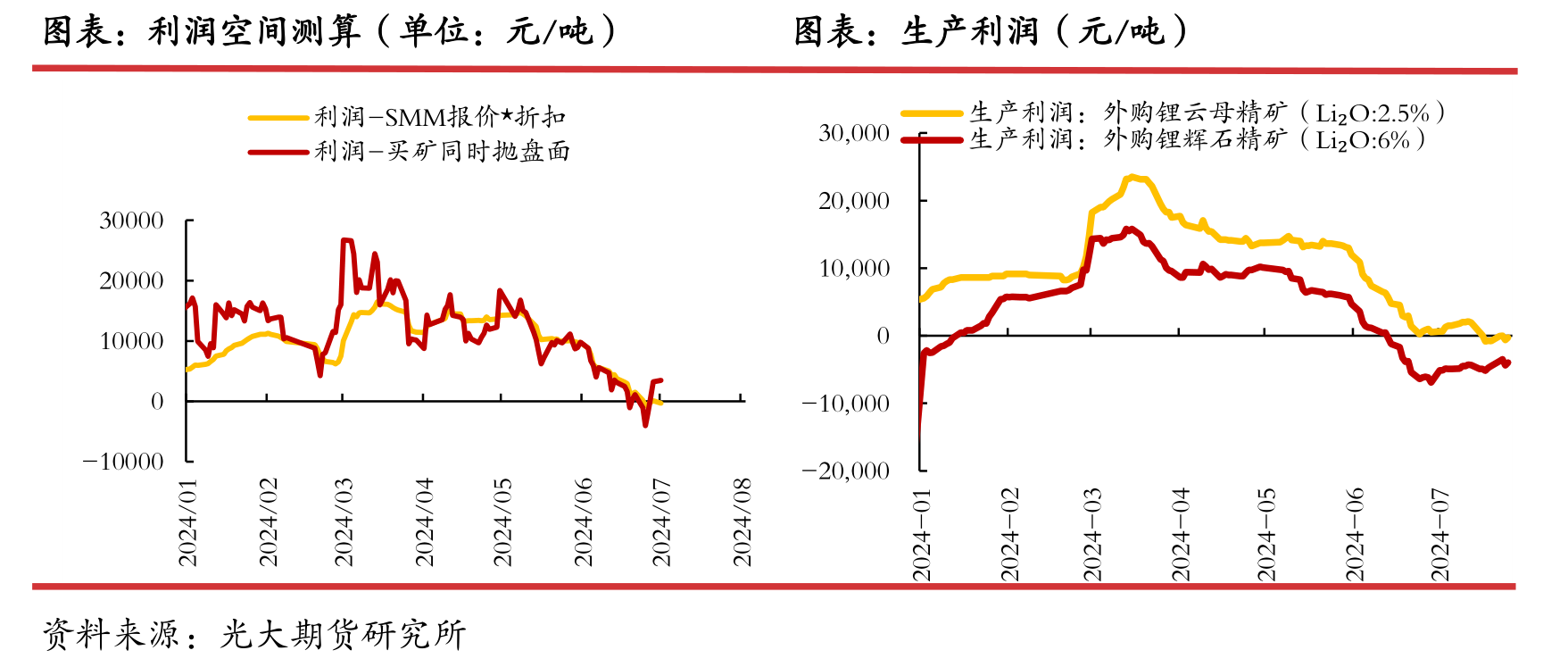
Therefore, from the perspective of profit driven production, the driving force has decreased.
The profit margin has been declining since May, and losses began to appear in mid to late June.
Some bulk ore traders have been suspended since the end of May, but the impact is relatively small.
Considering the shipping and processing periods, the actual reduction in August will gradually become apparent, which is also verified by the weekly production announced by SMS on August 1st.
For larger companies with relatively short-term losses or the inability to bring about substantial production shutdowns,
especially those that can obtain lower discount coefficients in long-term agreements,
but in the medium to long term, when lithium carbonate prices rapidly fall to the bottom range and fluctuate, there is significant uncertainty in profit margins.
If the losses persist for a long time, it may lead to production cuts.
2、 Explore cost support
The current price of lithium carbonate has dropped by 80000 yuan/ton, around the 90th percentile of the global lithium resource cost curve.
However, as the self-sufficiency rate of mines increases, the progress of mining projects on the right side of the cost curve has attracted much attention,
such as low-grade mica lithium extraction, some African ore lithium extraction, and some Australian ore lithium extraction projects.
In terms of lithium extraction from mica in Jiangxi, according to our previous research and visits, the cost of competitive projects in mica lithium extraction can reach 50000 yuan/ton,
while the complete cost of low-grade mica lithium extraction/semi self-sufficient lithium extraction projects is about 80000 to 90000 yuan/ton.
Although some newly launched projects cost over 100000 yuan per ton, their digestion channels are smooth, and their tolerance for lithium salt losses will be relatively high;
According to publicly available information, some non mining projects have high costs, exceeding 90000 yuan/ton, but there is still some room for decline in the future;
According to a research by Steel Union Australia, "Australian mining companies have stated that if the ore price is below $700/ton,
corresponding to a lithium carbonate price of 75000 to 80000 yuan/ton,
they will consider stopping production." "Based on the forecast of production in 2024, 80000 yuan/ton will be an important cost support for lithium carbonate.
At present, there has been no significant halt or reduction in production for mining projects with a total cost of over 80000 yuan/ton.
Furthermore, exploring cost support from the global balance sheet.
In 2024, the global supply of lithium resources will be approximately 1.406 million tons of LCE,
with a demand of approximately 1.21 million tons of LCE and an excess of approximately 195000 tons of LCE.
Demand accounts for about 86% of supply, with corresponding cost support of around 77000 yuan/ton.
However, it should be noted that lithium minerals are not completely converted into lithium carbonate,
and lithium mineral resources cannot be effectively converted into lithium salts.
Therefore, under more extreme assumptions, it is assumed that 70% of the resources will be converted into lithium carbonate (the remaining being lithium hydroxide,
lithium hexafluorophosphate, etc.), and a certain penalty coefficient will be given according to different quarters;
Assuming that the global demand for lithium carbonate accounts for 68-70%, the remaining is lithium hydroxide, lithium hexafluorophosphate, etc.
According to the adjusted data, the global demand for lithium carbonate accounts for about 84-86% of the supply,
with an excess of about 130000-160000 tons.
However, although global inventory is difficult to quantify, based solely on the current domestic inventory of lithium carbonate,
social inventory and exchange warehouse inventory may reach a level of over 140000 tons.
For example, according to Bloomberg, South Korea has begun to establish lithium inventories to ensure the supply of this critical mineral,
which is crucial for the battery and automotive manufacturing industries.
Therefore, assuming that China's lithium carbonate inventory accounts for 90% of the global total, which is about 155000 tons worldwide,
and based on this, considering that the inventory that can be produced accounts for 70%, there are about 108000 tons.
After excluding inventory levels, the actual supply may reach the 73-75% percentile of total resources, with an average resource cost of around 65000 yuan/ton corresponding to 74%.
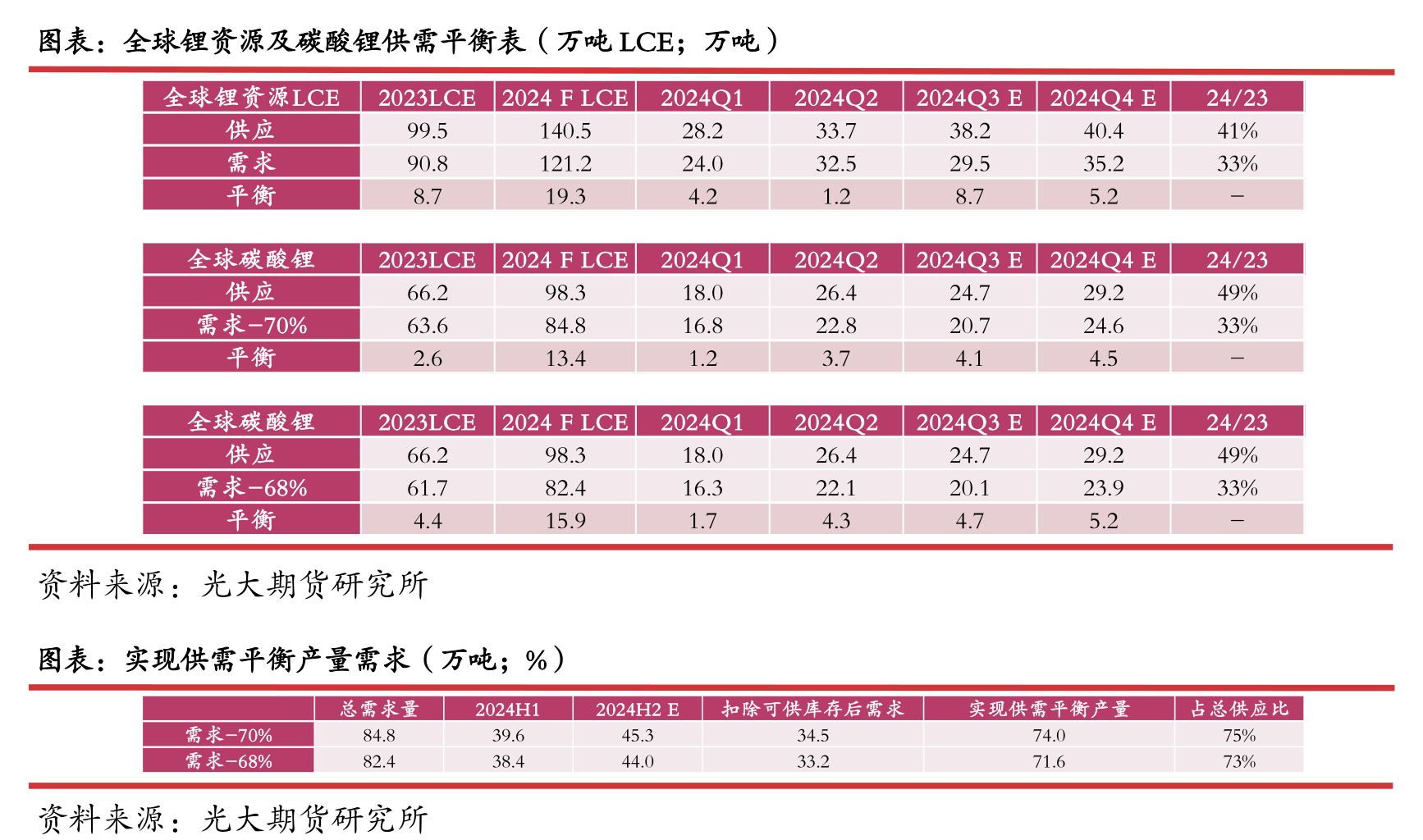
Given the increasing pricing power of lithium salts in the Chinese market,
if we only consider the supply-demand balance of lithium carbonate in China, the demand accounts for about 83.5% of the supply.
Compared with the global situation, the cost support in China is higher than the global level, which is largely driven by foreign mining and lithium extraction activities.
Assuming that the inventory of lithium carbonate available for production accounts for 30%, 50%, and 70% respectively,
achieving supply-demand balance will result in production accounting for approximately 79%, 76%, and 73% of the expected supply.
Therefore, if there is a reluctance to sell, it will to some extent raise the support below.
However, based on global resource costs, the cost difference between production capacities within the range of 73-79% is relatively small, the price push is average,
and reluctance to sell is not a long-term logic.
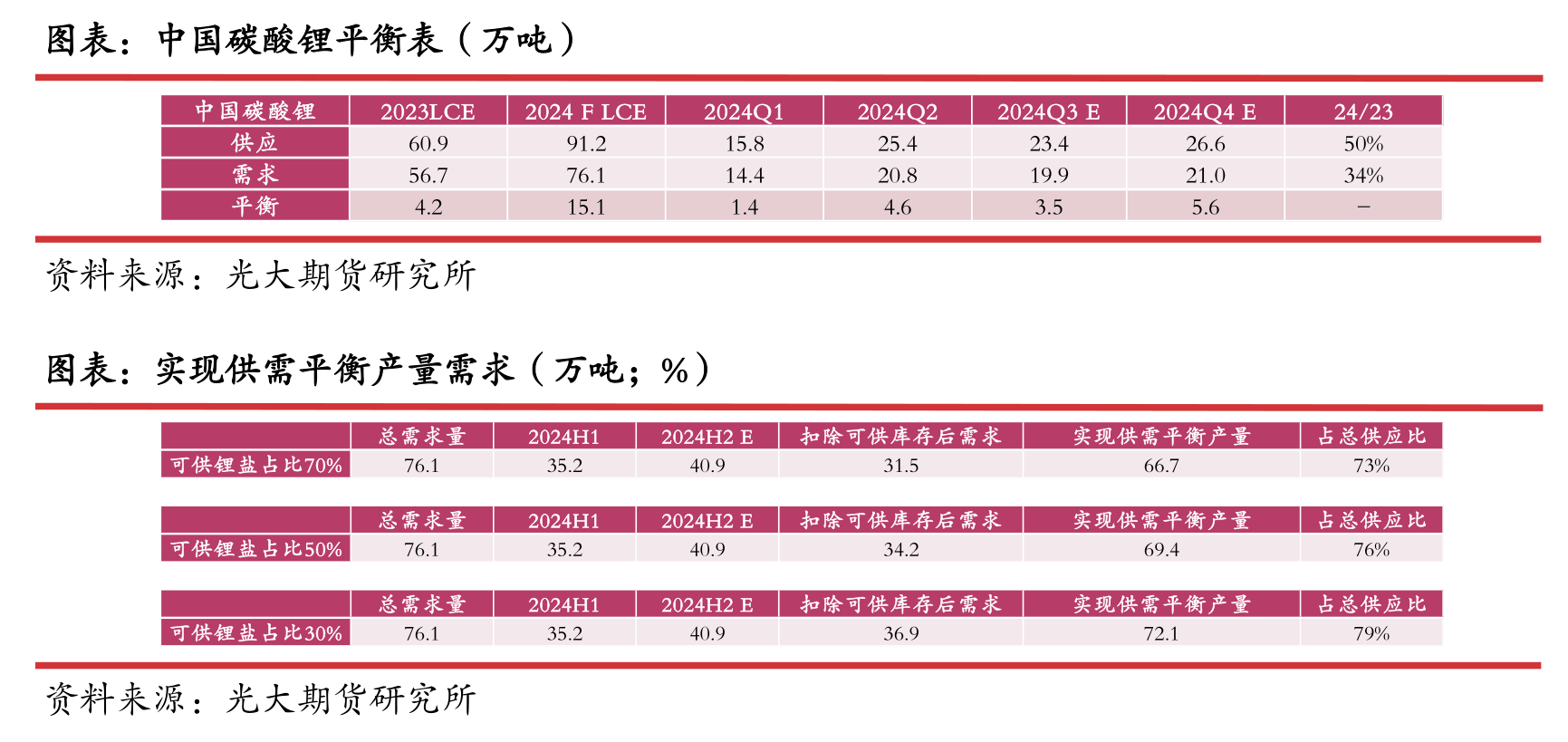
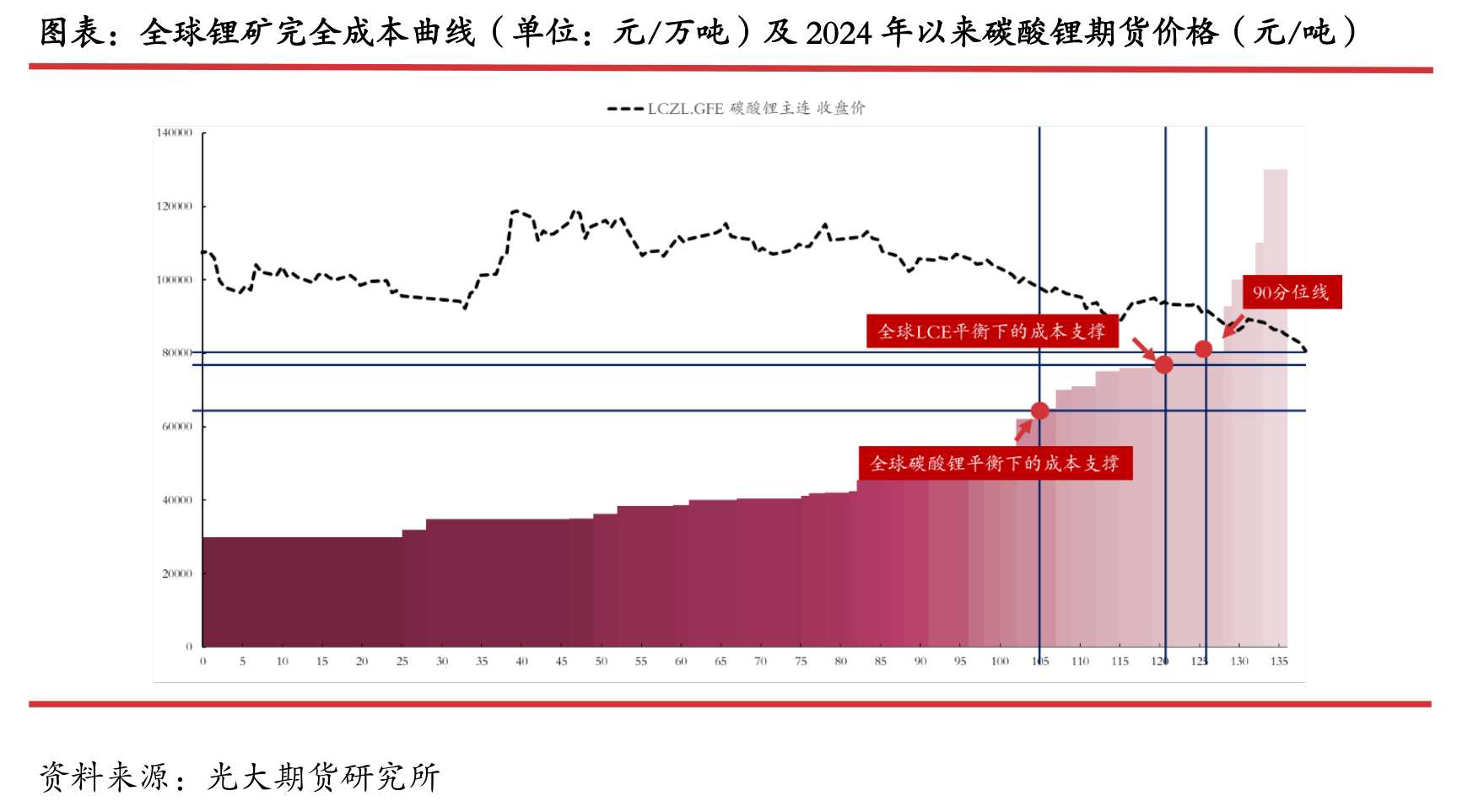
Therefore, we believe that when the price falls below 77000 yuan/ton, the intensity of supply side production reduction may gradually increase due to factors such as cost inversion and time,
thereby achieving the goal of marginal regulation of resource supply and demand, which will provide some support for the price.
Meanwhile, from the perspective of cost support under global lithium carbonate balance, it is at 65000 yuan/ton.
3、 Future prospects
Looking at the second half of the year, although there are still expectations of "golden September and silver October" and "year-end surge" demand in the market,
the temporary rebound in demand is indeed expected to drive the price center upward.
The expectation of replenishing inventory in August is still high, and the demand during the peak season is expected to drive a price rebound.
However, due to inventory pressure, we need to be relatively cautious about the strength of the rebound.
However, in reality, the global supply and demand pattern of lithium carbonate is difficult to reverse.
From the perspective of mining projects, the price support brought by higher cost projects is at 80000 yuan/ton, which is the 90th percentile of the full cost of the mine.
The global lithium resource supply-demand balance is estimated to have a marginal cost price of 77000 yuan/ton, which is approximately at the 86th percentile;
The global supply and demand balance of lithium carbonate is estimated to have a marginal cost price of 65000 yuan/ton, which is approximately at the 75th percentile.
Therefore, we believe that 80000 yuan/ton is the first cost support. If the short-term price drops below 80000 yuan/ton and rebounds,
it will not cause a significant reduction in production. However, if the long-term average price is at or below 77000 yuan/ton in the market,
it is more likely to trigger a contraction in supply.
If the price further drops,
market prices with a long-term average price of 65000 yuan/ton or less may be able to reverse the supply and demand structure through a significant reduction in mining production.
Risk Warning: Mines are reluctant to sell/exceeding expectations and stopping production; Demand rebounds beyond expectations






