Energy Storage | What is Lithium Battery?
Jul,29,24
What is a lithium battery?
The research on lithium batteries began in 1912 and it was not until 1970 that the first non rechargeable lithium battery was developed;
·In 1980, Goodenough et al. proposed a lithium rechargeable battery using cobalt oxide lithium as the positive electrode material, unveiling the prototype of lithium-ion batteries;
·In 1985, Akira Yoshino discovered carbon negative electrode materials based on Goodenough's negative electrode and manufactured the first commercially viable lithium-ion battery;
·The prototype design of lithium-ion batteries was completed in 1986;
·In 1991, SONY and Moli companies from Japan collaborated to produce a commercial lithium-ion battery using LiCoO as the positive electrode material and carbon black as the negative electrode material.
Lithium battery refers to a battery that contains lithium (including metallic lithium, lithium alloys, lithium ions, and lithium polymers) in an electrochemical system.
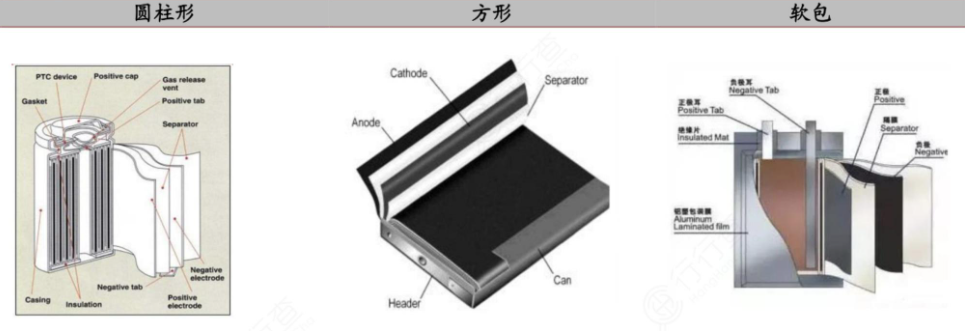
Lithium batteries can be roughly divided into two categories: lithium metal batteries and lithium-ion batteries.
Lithium metal batteries are usually non rechargeable and typically use manganese dioxide as the positive electrode material, metallic lithium or its alloy metal as the negative electrode material,
and non-aqueous electrolyte solution.
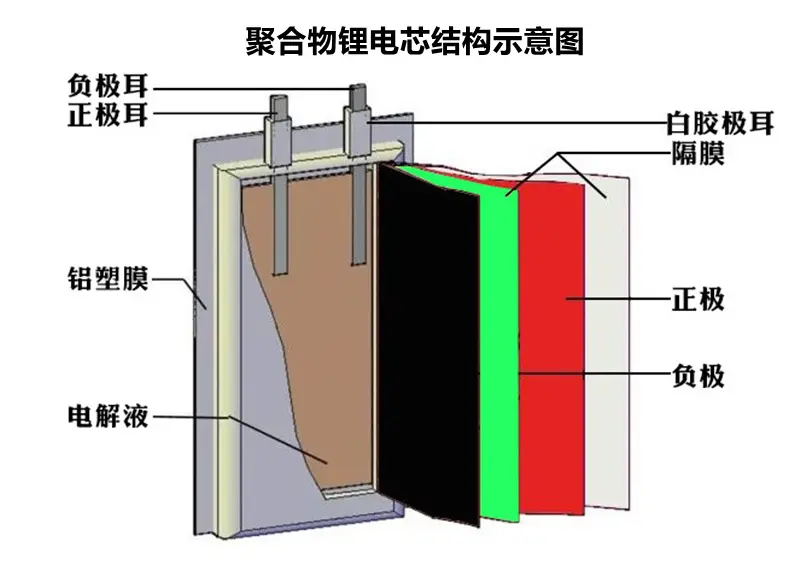
Lithium ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that typically use lithium alloy metal oxides as positive electrode materials, graphite as negative electrode materials, and non-aqueous electrolytes.
Main advantages of lithium batteries:
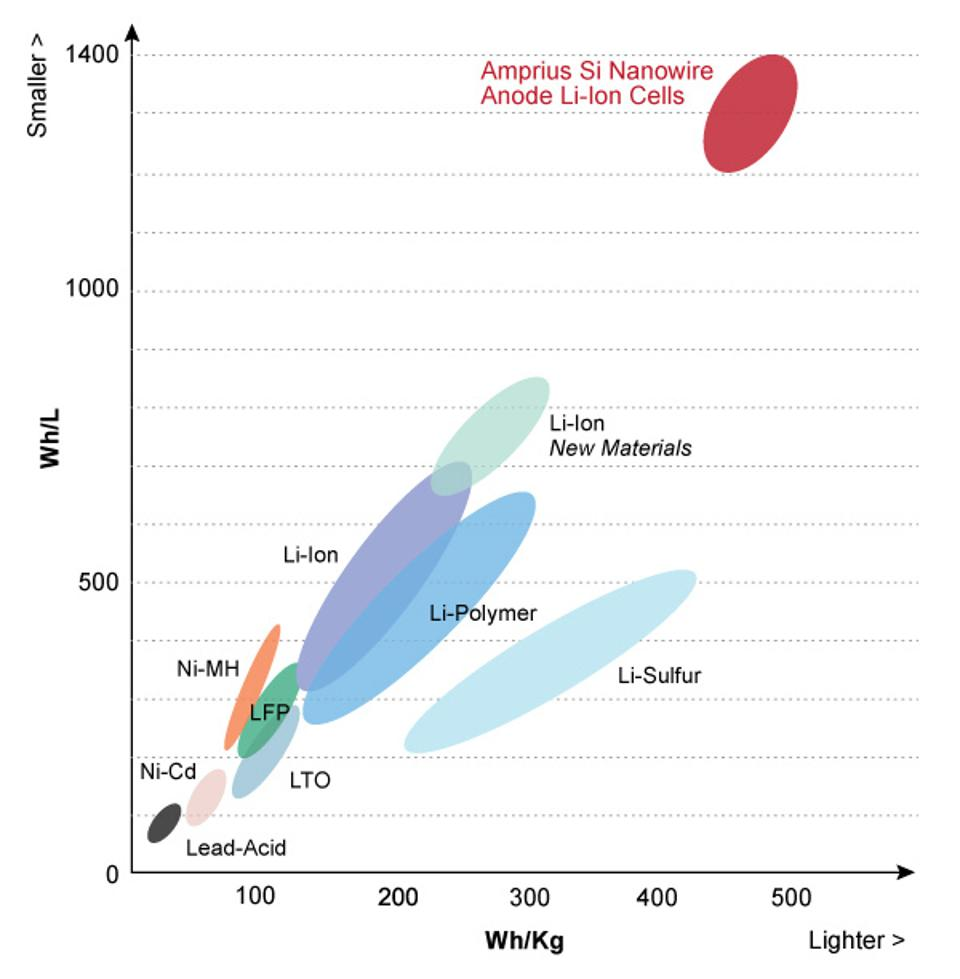
1. It has high energy density and high storage capacity, currently reaching 460-600Wh/kg, which is about 6-7 times that of lead-acid batteries;
2. Long service life, with a service life of over 6 years. The battery with lithium iron phosphate as the positive electrode can be charged and discharged at 1C (100% DOD), with a record of 10000 uses;
3. High rated voltage (single working voltage of 3.7V or 3.2V), approximately equal to the series voltage of three nickel cadmium or nickel hydrogen rechargeable batteries,
making it easy to form a battery power pack;
4. It has high power bearing capacity, among which the lithium iron phosphate lithium-ion battery used in electric vehicles can achieve the ability to charge and discharge at 15-30 ° C,
which is convenient for high-intensity starting acceleration;
5. The self discharge rate is very low, which is one of the most prominent advantages of this battery.
Currently, it can generally achieve less than 1% per month, which is less than 1/20 of nickel hydrogen batteries;
6. Lightweight, with a weight of about 1/6-1/5 of lead-acid products under the same volume;

7. Strong adaptability to high and low temperatures, can be used in environments ranging from -20 ℃ to 60 ℃, and after processing, can be used in environments ranging from -45 ℃;
8. Green and environmentally friendly, regardless of production, use, or disposal,
it does not contain or produce any toxic or harmful heavy metal elements or substances such as lead, mercury, cadmium, etc.
What are the positive and negative electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium ion batteries are mainly composed of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, an electrolyte, and a battery casing.
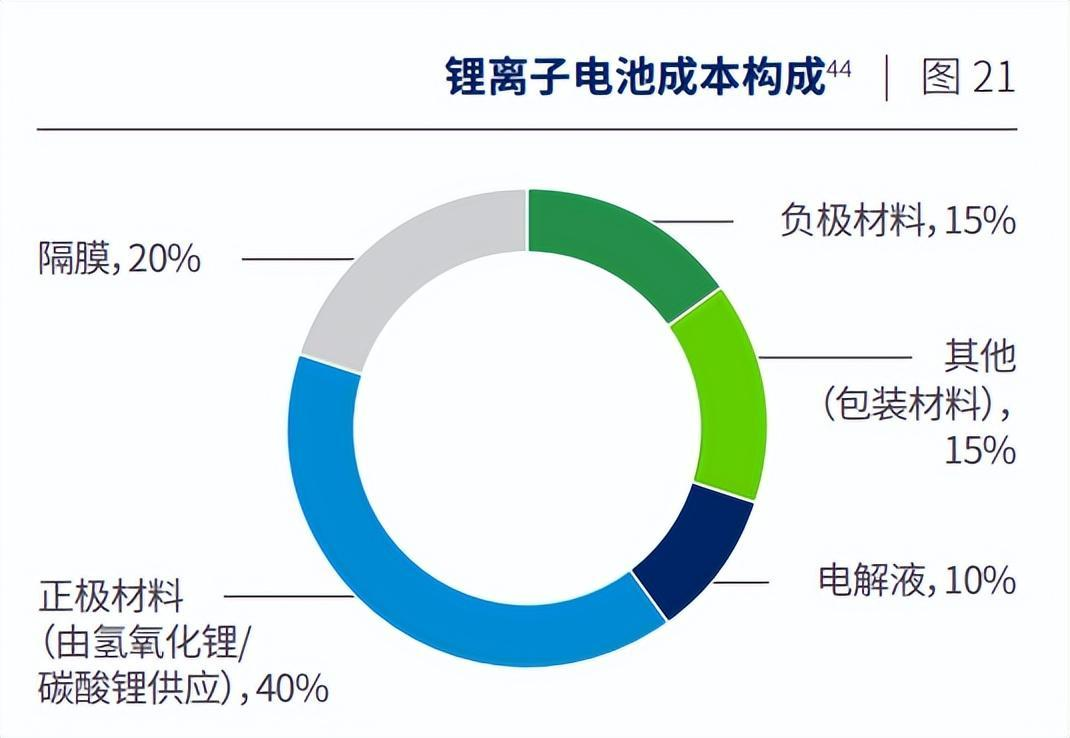
The positive electrode material is in the most critical position, and lithium batteries are generally named after the positive electrode material.
Positive electrode material is the most expensive raw material in batteries.
The positive electrode material provides the lithium ions required for the electrochemical reaction of the battery.
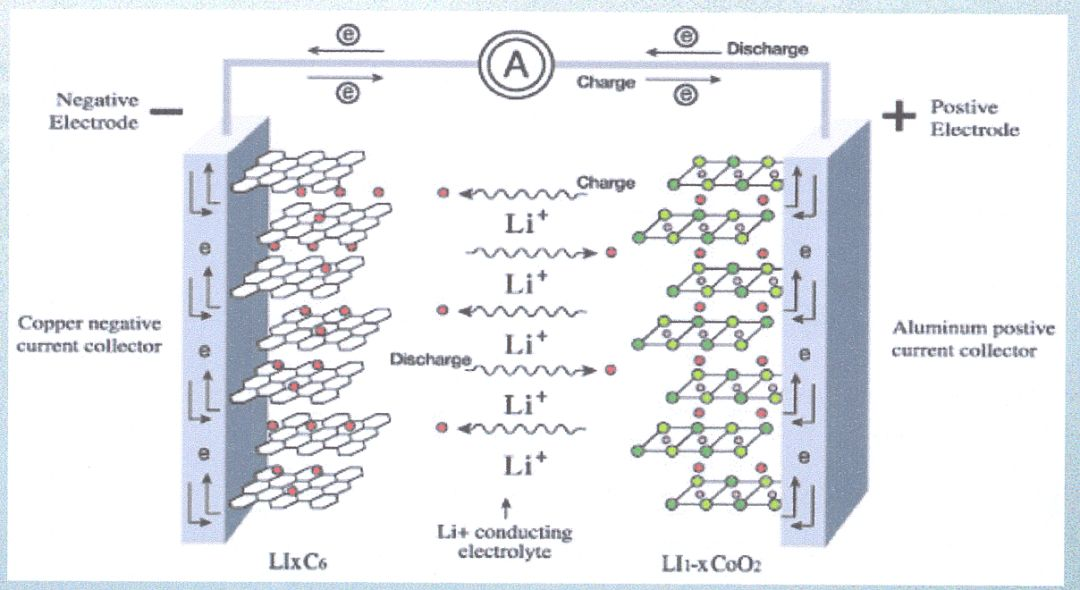
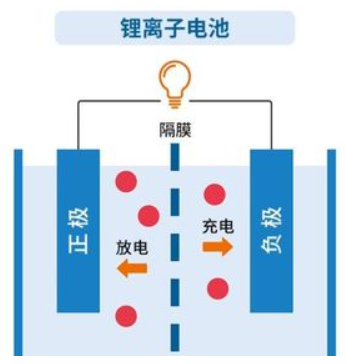
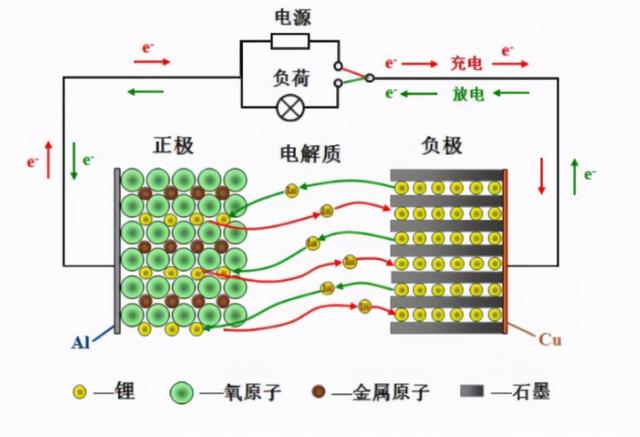
Lithium ion batteries rely on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes to achieve charging and discharging.
During the charging process, lithium ions are released from the positive electrode and embedded in the negative electrode.
During the discharging process, lithium ions are released from the negative electrode and returned to the positive electrode, completing a charging and discharging process.
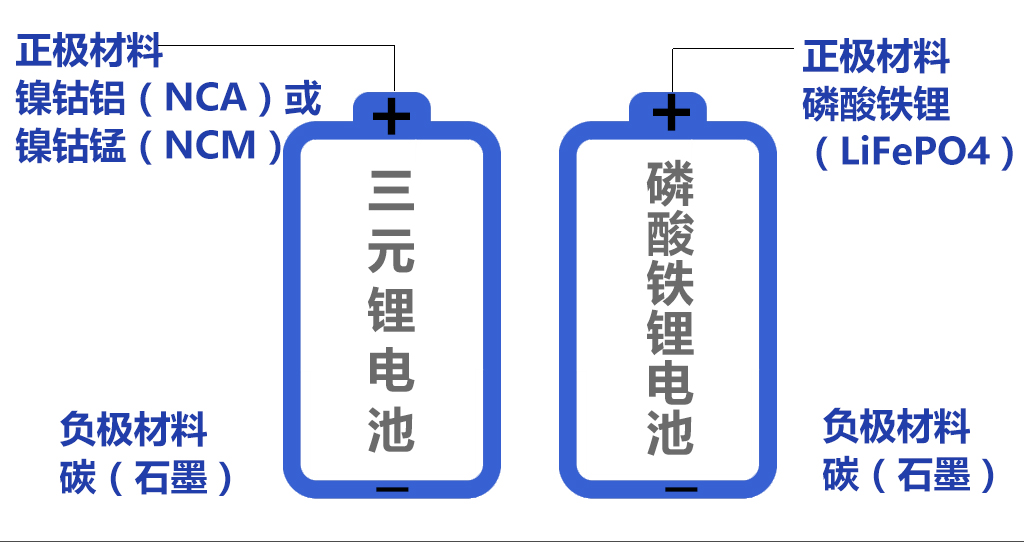
The positive electrode materials mainly include four types: lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, lithium iron phosphate,
and ternary materials (including nickel cobalt manganese potassium NCM and nickel cobalt aluminum NCA).
Among them, lithium iron phosphate and ternary materials are more important. Ternary materials have high energy density, long battery life, safer, lower cost, and longer lifespan.

The negative electrode material of lithium-ion batteries is an important component of lithium-ion batteries.
The negative electrode active material is graphite or carbon silicon materials with a graphite like structure.

Negative electrode materials are generally divided into carbon based negative electrodes and non carbon based negative electrodes,
among which carbon based negative electrodes can be divided into graphite, hard carbon, soft carbon negative electrodes, etc.
Graphite can be divided into artificial graphite, natural graphite, composite graphite, and intermediate phase carbon microspheres;
Non carbon negative electrodes include lithium titanate, tin based alloy negative electrodes, silicon-based negative electrodes, etc.






