A co embedded high-voltage lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material and its preparation method
Aug,01,24
The positive electrode materials for new energy vehicle power batteries are mainly ternary and lithium iron phosphate.
Ternary batteries have the advantages of good low-temperature performance, high energy density, and charging efficiency,
while lithium iron phosphate has better safety and long cycle performance.
With the development of technology and policies, the market share of lithium iron phosphate power batteries has gradually approached 70%.
However, lithium iron phosphate materials have always had the problem of low compaction density (the powder compaction density of industrialized lithium iron phosphate cathode materials is generally 2.4-2.45g/cm3).
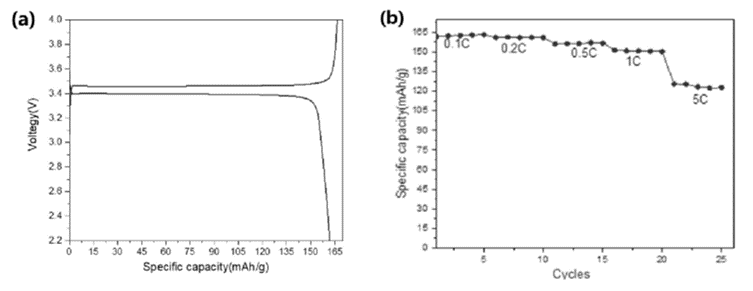
For the positive electrode material of lithium-ion batteries, the higher the powder compaction density, the higher the capacity of lithium-ion batteries can be achieved.
The known technical solutions for improving the compaction density of lithium iron phosphate mainly include increasing the calcination temperature of the material,
extending the calcination time, reducing the carbon coating amount of the material, optimizing the particle size distribution of the material through grinding schemes, etc.
However, the existing technical solutions have the following technical problems:
(1) Increasing the sintering temperature and prolonging the calcination time of lithium iron phosphate essentially increases the primary particle size of the positive electrode material.
Although it is beneficial for improving the powder compaction density of the material, it will seriously reduce the electrochemical performance of the material;
(2) Reducing the amount of carbon coating will decrease the conductivity of the material and directly reduce its electrochemical performance;
(3) Optimizing the particle size ratio to increase the compaction density of materials is generally a complex operation.
In the conventional preparation method of lithium iron phosphate,
improving the compaction density and excellent electrochemical performance of lithium iron phosphate often cannot be achieved simultaneously.
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a co embedded high-voltage solid lithium iron phosphate cathode material and its preparation method,
which solves the problem of low compaction density or loss of electrochemical performance in the preparation of existing lithium iron phosphate.
The method comprises the following steps: mixing lamellar ferric phosphate with a carbon source, carrying out a first grinding treatment to obtain a first grinding slurry,
drying the first grinding slurry with spray, and carrying out a first calcination treatment to obtain a pre calcined slurry;
Grind and mix the pre burned material with granular iron phosphate to obtain a mixture.
Add carbon and lithium sources to the mixture for a second grinding treatment to obtain a second grinding material;
After drying the second abrasive, a second calcination treatment is performed to obtain lithium iron phosphate cathode material.
Firstly, pre coating the sheet-like precursor with a carbon source can improve the effectiveness of the initial carbon coating.
Then, mixing the granular precursor for secondary coating can improve the uniformity of the overall carbon coating structure and overcome defects caused by morphological differences;
Beneficial for improving the uniformity of the overall carbon coating of the material, thereby achieving better conductivity.
Related figures:
Figure 1:
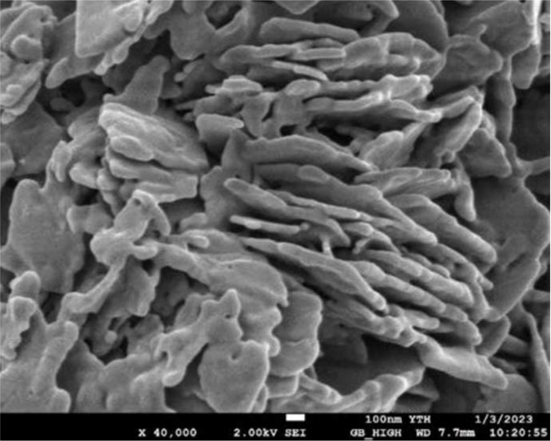
Figure 2:
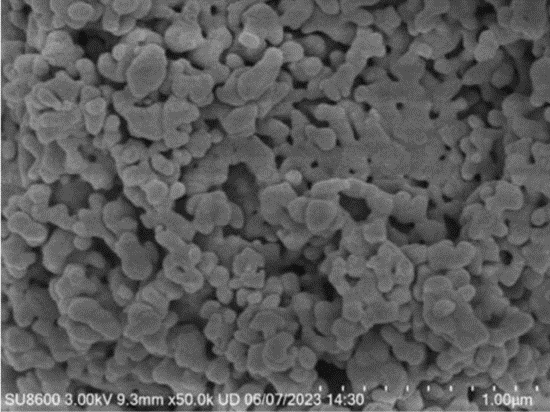

Figure 3:
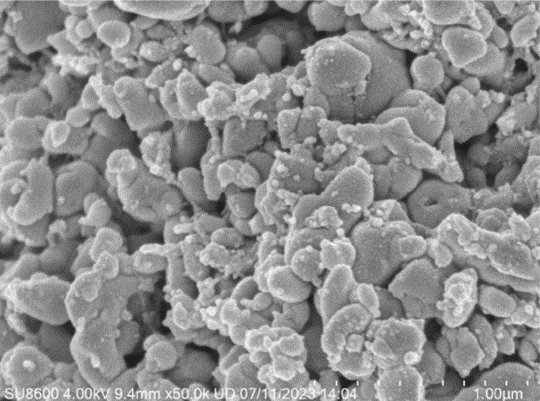

Figure 4: